The Traditional Payment Problem
Understanding the limitations and friction points of traditional payment systems.
The Payment Friction Problem
Traditional payment systems create significant friction for both users and developers, especially when dealing with digital services, APIs, and content. This friction manifests in multiple ways, making it difficult to implement efficient payment models for modern applications.
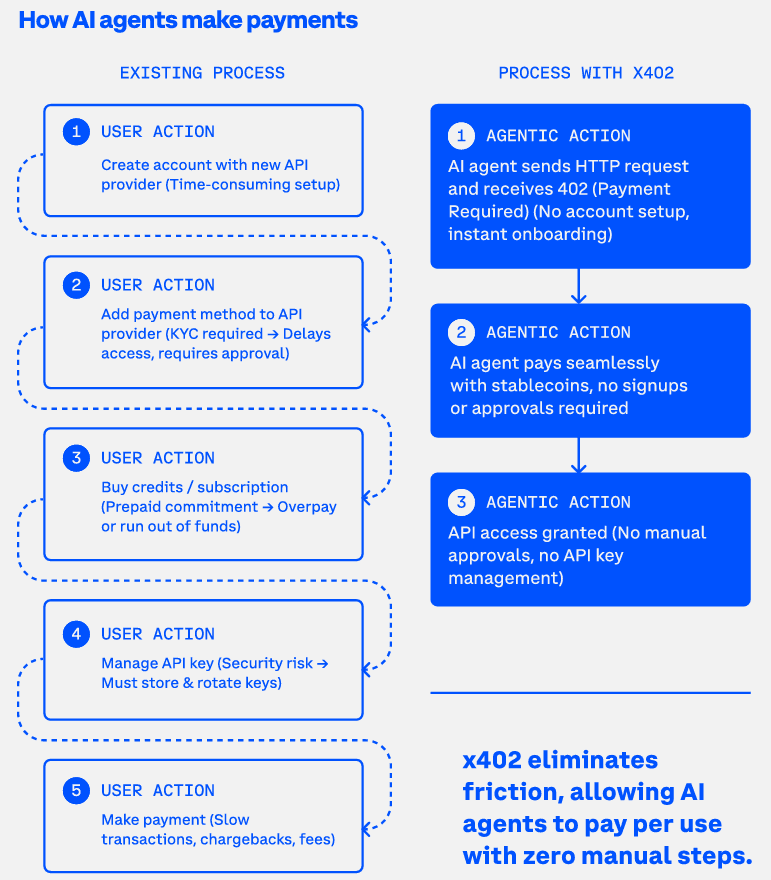
The Five-Step Friction Model
Every traditional payment interaction requires users to complete at least five time-consuming steps:
1. Create Account
Before making any payment, users must:
- Sign up for a service account
- Provide personal information
- Verify email addresses
- Set up passwords and security
Time Impact: 5-15 minutes per service
User Experience: High abandonment rates during signup
2. Add Payment Method
After creating an account, users must:
- Enter credit card details
- Complete bank verification
- Wait for payment method approval
- Navigate complex payment forms
Time Impact: 3-10 minutes
User Experience: Security concerns and data privacy issues
3. Complete KYC (Know Your Customer)
Many services require additional identity verification:
- Submit government-issued ID
- Provide proof of address
- Complete video verification
- Wait for manual approval
Time Impact: Hours to days
User Experience: Privacy concerns and verification delays
4. Buy Credits or Subscribe
Traditional payment models force prepayment:
- Purchase credits you may not use
- Subscribe to monthly plans
- Commit to minimum purchases
- Lock in before trying the service
Time Impact: Variable
User Experience: Financial commitment before knowing value
5. Manage API Keys
For API access, developers must:
- Generate and store API keys
- Implement key rotation policies
- Secure keys in environment variables
- Monitor for key compromise
Time Impact: Ongoing maintenance
User Experience: Security risk and complexity
Cost Structure Problems
Traditional payment processors impose significant fees that make micropayments impractical:
High Percentage Fees
- Credit card processors: 2.9% + $0.30 per transaction
- PayPal: 3.49% + fixed fee
- Stripe: 2.9% + $0.30 per transaction
Impact on Micropayments: For a $0.01 API request, traditional fees would be $0.32 (3,200% overhead)
Fixed Fee Floor
The fixed fee component ($0.30) makes transactions under $10 economically unviable for merchants.
Settlement Delays
Payment processors hold funds for 2-7 days, creating cash flow challenges for merchants and limiting real-time business models.
Barriers to Automation
Traditional payments were designed for human-to-merchant interactions, not for automated systems. This creates fundamental barriers:
- Manual Account Setup: Automated systems cannot complete human-centric signup flows (CAPTCHA, email verification, identity checks)
- Credential Management: Storing payment credentials creates security and compliance risks
- Pre-Approval Requirements: Automated payments require human authorization, preventing autonomous operation
These barriers make it impossible for AI agents and automated systems to participate in the payment economy.
The Micropayment Impossibility
Traditional payment systems make micropayments economically impossible:
Transaction Value: $0.01 (1 cent API request)
Processing Fee: 2.9% + $0.30
Total Fee: $0.30029
Net to Merchant: -$0.29029 (loss of 2,903%)
Result: Merchant loses money on every transactionThis economic reality forces developers into subscription models even when pay-per-use would better serve users.
The API Monetization Challenge
Developers face a painful choice when monetizing APIs:
Option 1: Free with Rate Limits
- No revenue
- Abuse potential
- Resource waste
- Unsustainable scaling
Option 2: Monthly Subscriptions
- High user commitment barrier
- Revenue from unused capacity
- All-or-nothing pricing
- Poor user experience for occasional users
Option 3: Traditional Payments
- High fees eliminate profitability
- Complex integration
- Slow settlement
- User friction
None of these options are optimal, creating a gap in the market for pay-per-use API models.
The AI Agent Problem
As AI agents become more prevalent, traditional payment systems create impossible barriers:
AI Agents Cannot:
- Create Accounts: Most signup flows require human verification (CAPTCHA, email confirmation)
- Complete KYC: Identity verification is designed for humans, not autonomous agents
- Store Credentials Securely: API keys and payment tokens create security vulnerabilities
- Make Autonomous Decisions: Pre-approved payment methods limit AI flexibility
- Handle Micropayments: Transaction fees make small payments impossible
What AI Agents Need:
- Instant, permissionless access to resources
- Pay-per-use pricing with no minimums
- Autonomous payment execution
- No account creation or KYC
- Micropayment support (fractions of a cent)
Real-World Impact
These limitations have real consequences:
For Developers
- Cannot monetize APIs effectively
- Forced into subscription models
- High payment processing overhead
- Limited business model flexibility
For Users
- Must prepay for uncertain value
- Create accounts for one-time use
- Share payment details with many services
- Pay for unused capacity
For AI Builders
- Cannot create autonomous payment systems
- Limited to pre-approved payment rails
- Unable to enable AI-to-AI commerce
- Forced into complex workarounds
The Need for a New Approach
Traditional payment systems were designed for a different era—before micropayments, before API economies, and before AI agents. We need a payment protocol that:
- Eliminates Account Requirements: Instant, permissionless access
- Supports Micropayments: Economically viable payments of any size
- Enables Automation: AI agents can pay autonomously
- Settles Instantly: No 2-7 day delays
- Charges Fairly: No percentage fees or high fixed costs
- Works with HTTP: Native integration with web infrastructure
This is exactly what the x402 protocol provides.
Summary
Traditional payment systems create insurmountable barriers for modern digital commerce through account requirements, high fees, settlement delays, and automation limitations. These systems make micropayments impossible, force developers into suboptimal business models, and prevent AI agents from participating in the economy. The x402 protocol addresses all of these limitations by providing instant, permissionless, HTTP-native payments with minimal fees.
Is this guide helpful?
